
DATE PUBLISHED: November 8, 2024
Shareholder Proposals on Nature: Resurgence and New Frameworks
Corporate impacts and dependencies related to nature have garnered considerable attention in recent years, with growing interest also reflected in shareholder proposal campaigns focused on nature-related issues. The landmark 2022 COP 15 summit that established the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, the launch of the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) in 2021, and the inclusion of Biodiversity and Ecosystems as key reporting standard under the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) per the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) are among the key drivers for the reframing of the discussion around nature and renewed interest in environmental impacts and relevant disclosures.
With the 16th Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (COP 16) currently underway, ISS-Corporate reviewed nature-themed shareholder proposals during the past decade to identify key trends and developments related to nature in corporate shareholder engagements.
Resurgence in Nature-Related Shareholder Proposal Volume, High Rate of Withdrawals, but Lower Support
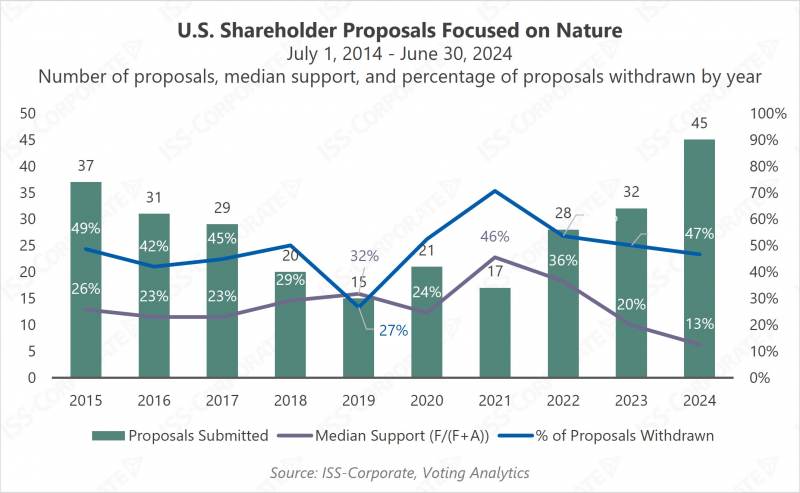
Proposals focusing on environmental impacts have long held a meaningful position on the agenda in shareholder engagements dealing with sustainability risks. Until recently, as climate change-related proposals dominated the conversation, the volume of other environmental proposals subsided. However, the past three years have seen a resurgence on nature-related shareholder proposals, with a record number of 45 submitted requests at U.S. companies in the twelve months leading to June 30, 2024. Support levels peaked in 2021, with voted proposals reaching a median level of support of 46% of votes cast. In the same year, 71% of submitted proposals were withdrawn by proponents, indicating successful engagements and likely commitments by companies to improve disclosures or practices.
While volumes have risen in recent years, support levels have dropped significantly, with median support among voted proposals standing at 13% of votes cast in 2024, primarily due to companies already substantially addressing the proponents’ requests. However, nature-related proposals continue to gain traction off the ballot, as withdrawal rates remain high, with 47% of proposals withdrawn in 2024.
Shareholder Proposals Adopting New Nature Framework
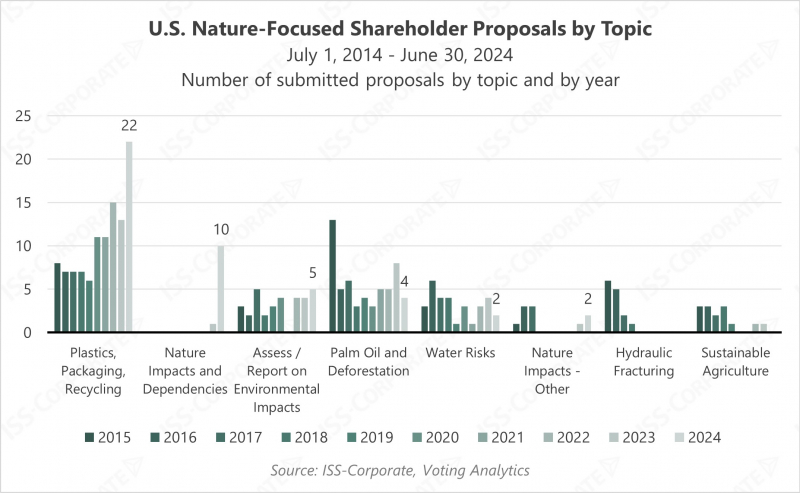
In the most recent proxy season, one of the key trends related to nature-oriented proposals pertains to the adoption of new frameworks for managing and reporting on nature and biodiversity impacts. In the twelve-month period leading to June 30, 2024, 10 submitted proposals asked companies to report on their nature and biodiversity impacts, dependencies, risks, and opportunities, effectively suggesting companies report in line with the TNFD framework and along the lines of the ESRS standards. This type of reporting takes a holistic assessment of the company’s nature-related dependencies and impacts and facilitates strategy development to manage associated risks in operations and along the value chain.
In previous years, submitted proposals tended to be relatively narrow in scope, focusing on specific corporate impacts. Such requests included questions around deforestation in the supply chain, the impacts of hydraulic fracturing, the environmental and health impacts of coal ash, the impacts of pesticides on pollinators, water pollution from specific operations, drilling in the Arctic, the use of polystyrene foam cups, and other operations-specific concerns. While proponents continue to raise many of these specific questions, the numbers of such proposals have either plateaued or decreased. Proposals focusing on packaging, recycling, and the use of plastics are the exception, as they have grown in numbers, reaching a record of 22 proposals in 2024.
Consumer Companies Get Most Nature-Related Shareholder Proposals
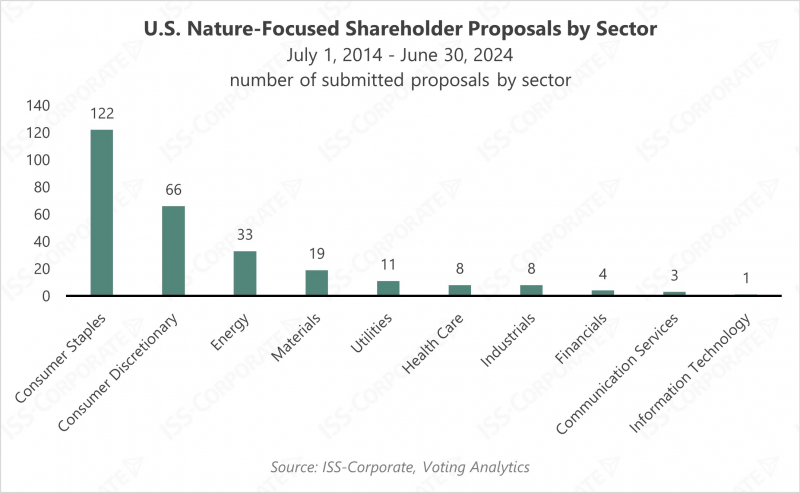
During the decade under review, 68% of submitted nature-related proposals targeted the consumer goods sectors, with questions related to plastics, packaging, and deforestation making the largest portion these requests. Companies in the energy and materials sectors have also received a meaningful number of proposals focusing on nature impacts. However, as perspectives and reporting expectations around nature impacts and dependencies evolve, companies in other sectors may receive more questions related to their assessment and management of such risks through newly established frameworks, especially considering impacts along the value chain.
Integrating Nature in a Broader Corporate Sustainability Strategy
As companies begin to capture nature dependencies and impacts in their corporate sustainability strategies and reporting, they stand to benefit from a more comprehensive assessment of material issues, but they also likely face new challenges and complexities in conducting this exercise. That said, many resources are becoming available to help companies navigate their nature-related risks, including the newly established frameworks as well as many open access nature databases and relevant risk assessment tools. As nature impacts tend to be interlinked with other key issues, such as climate change, environmental justice, and community impact, companies may find opportunities to enhance their broader sustainability strategies by leveraging these newer frameworks and resources.

